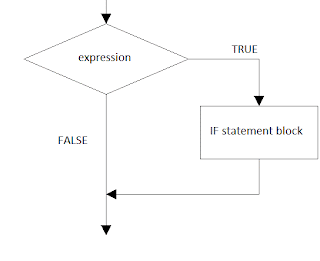
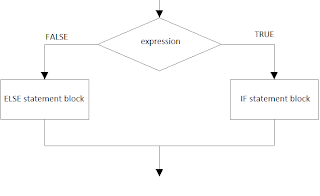
Enumeration are declared using enum keyword. Enumeration are distinct type consisting of a set of names that are constant.
For example we know that days in week are constant so we can use enum for days and month also.
Each enum type has a corresponding integral type called the underlying type of the enum
type. This underlying type must be able to represent all the enumerator values defined in
the enumeration. An enum declaration may explicitly declare an underlying type of byte,
sbyte, short, ushort, int, uint, long, or ulong. Note that char cannot be used as an underlying
type. An enum declaration that does not explicitly declare an underlying type has an
underlying type of int.
Example:-
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace test_practise
{
public enum Days { Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday, Sunday }
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Days day = Days.Monday;
Console.WriteLine((int)day);
Console.WriteLine(day);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
You will see output 0. You can change the value of Monday from 0 to 1 by assigning value to Monday
public enum Days { Monday=1, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday, Sunday }
For example we know that days in week are constant so we can use enum for days and month also.
Each enum type has a corresponding integral type called the underlying type of the enum
type. This underlying type must be able to represent all the enumerator values defined in
the enumeration. An enum declaration may explicitly declare an underlying type of byte,
sbyte, short, ushort, int, uint, long, or ulong. Note that char cannot be used as an underlying
type. An enum declaration that does not explicitly declare an underlying type has an
underlying type of int.
Example:-
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace test_practise
{
public enum Days { Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday, Sunday }
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Days day = Days.Monday;
Console.WriteLine((int)day);
Console.WriteLine(day);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
You will see output 0. You can change the value of Monday from 0 to 1 by assigning value to Monday
public enum Days { Monday=1, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday, Sunday }